1.给出多个图像(二维矩阵),求出满足阈值的中风区域。
2.主要是考察并查集。
3.每输入一个像素点,就检测它的上边,左边,上一层的位置是否为1,为1的话,归为一个集合。
4.最后对集合的数量进行统计。
One important factor to identify acute stroke (急性脑卒中) is the volume of the stroke core. Given the results of image analysis in which the core regions are identified in each MRI slice, your job is to calculate the volume of the stroke core.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains 4 positive integers: M, N, L and T, where M and N are the sizes of each slice (i.e. pixels of a slice are in an M by N matrix, and the maximum resolution is 1286 by 128); L (<=60) is the number of slices of a brain; and T is the integer threshold (i.e. if the volume of a connected core is less than T, then that core must not be counted).
Then L slices are given. Each slice is represented by an M by N matrix of 0’s and 1’s, where 1 represents a pixel of stroke, and 0 means normal. Since the thickness of a slice is a constant, we only have to count the number of 1’s to obtain the volume. However, there might be several separated core regions in a brain, and only those with their volumes no less than T are counted. Two pixels are “connected” and hence belong to the same region if they share a common side, as shown by Figure 1 where all the 6 red pixels are connected to the blue one.
 Figure 1
Figure 1For each case, output in a line the total volume of the stroke core.
Sample Input:
3 4 5 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0
Sample Output:
26
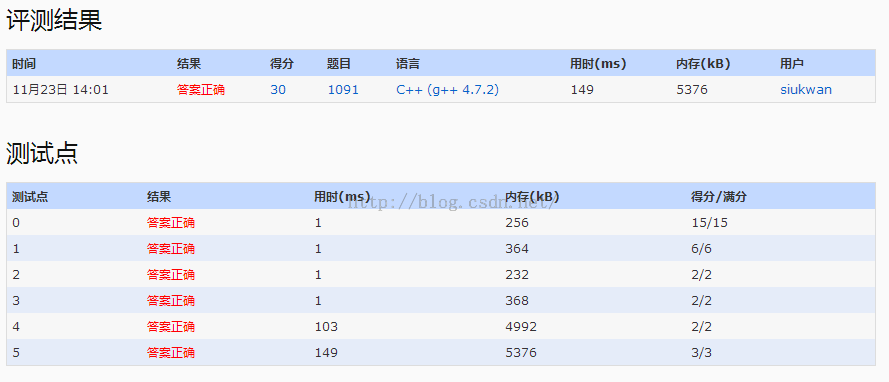
AC代码:
[c language=”++”]
//#include<string>
//#include <iomanip>
//#include<stack>
//#include<unordered_set>
//#include <sstream>
//#include "func.h"
//#include <list>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<set>
#include<queue>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<memory.h>
#include<limits.h>
using namespace std;
int find(int*r, int x)
{
for (; x != r[x]; x = r[x])
r[x] = r[r[x]];
return r[x];
}
int find(vector<int>&r, int x)
{
for (; x != r[x]; x = r[x])
r[x] = r[r[x]];
return r[x];
}
int main(void)
{
int m,n,l,t;//1286,128,60
cin >> m >> n >> l >> t;
char *image = new char[m*n*l];
memset(image, 0, sizeof(image));
//int *r = new int[m*n*l];
//memset(r, -1, sizeof(r));
vector<int> r(m*n*l, -1);
for (int k = 0; k < l; k++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int tmp = k*(m*n) + j*n + i;
scanf("%d", &image[k*(m*n) + j*n + i]);
if (image[k*(m*n) + j*n + i] == 1)
{
if (r[k*(m*n) + j*n + i] == -1)//如果为-1,则还没初始化代表,进行初始化代表为自己
r[k*(m*n) + j*n + i] = k*(m*n) + j*n + i;
if (i>0 && image[k*(m*n) + j*n + (i – 1)] == 1)
{//上面
r[find(r, k*(m*n) + j*n + i)] = find(r, k*(m*n) + j*n + (i – 1));
}
if (j>0 && image[k*(m*n) + (j-1)*n + i] == 1)
{//左边
r[find(r, k*(m*n) + j*n + i)] = find(r, k*(m*n) + (j – 1)*n + i);
}
if (k>0 && image[(k-1)*(m*n) + j*n + i] == 1)
{//上一层
r[find(r, k*(m*n) + j*n + i)] = find(r, (k – 1)*(m*n) + j*n + i);
}
}
}
}
}
map<int, int> hash;
int sum = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < l; k++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (image[k*(m*n) + j*n + i] == 1)
{
int tmp = find(r, k*(m*n) + j*n + i);
hash[tmp]++;
if (hash[tmp] == t)
sum += t;
else if (hash[tmp] > t)
sum++;
}
}
}
}
cout << sum << endl;
return 0;
}
[/c]