1.这道题目实则是一道关于的题目,树的每一层代表一个级别的供应商,树的高度越大,价格越高
如题目例子:
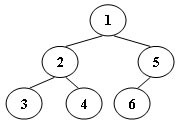
9 1.80 1.00 1 5 4 4 -1 4 5 3 6
构成的树为
红色部分(0和8,两个)的价格最高,为1.8*1.01*1.01*1.01=1.85。
2.采用合适的数据结构存储节点,然后BFS进行层次遍历即可。
A supply chain is a network of retailers(零售商), distributors(经销商), and suppliers(供应商)– everyone involved in moving a product from supplier to customer.
Starting from one root supplier, everyone on the chain buys products from one’s supplier in a price P and sell or distribute them in a price that is r% higher than P. It is assumed that each member in the supply chain has exactly one supplier except the root supplier, and there is no supply cycle.
Now given a supply chain, you are supposed to tell the highest price we can expect from some retailers.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, The first line contains three positive numbers: N (<=105), the total number of the members in the supply chain (and hence they are numbered from 0 to N-1); P, the price given by the root supplier; and r, the percentage rate of price increment for each distributor or retailer. Then the next line contains N numbers, each number Si is the index of the supplier for the i-th member. Sroot for the root supplier is defined to be -1. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print in one line the highest price we can expect from some retailers, accurate up to 2 decimal places, and the number of retailers that sell at the highest price. There must be one space between the two numbers. It is guaranteed that the price will not exceed 1010.
Sample Input:
9 1.80 1.00 1 5 4 4 -1 4 5 3 6
Sample Output:
1.85 2
AC代码:
[c language=”++”]
//#include<string>
//#include <iomanip>
#include<vector>
#include <algorithm>
//#include<stack>
#include<set>
#include<queue>
#include<map>
//#include<unordered_set>
#include<unordered_map>
//#include <sstream>
//#include "func.h"
//#include <list>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<memory.h>
#include<limits.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
vector<int> list;
Node() :list(0){};
};
int main(void)
{
int n;
double rootPrice;
double higherPercent;
cin >> n >> rootPrice >> higherPercent;
vector<Node> supplier(n);
int root;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int Si;
scanf("%d", &Si);
if (Si == -1) root = i;//-1为根供应商
else//i的上级供应商为Si
supplier[Si].list.push_back(i);
}
//进行层次遍历
queue<int> q;
int count1 = 1, count2 = 0;
q.push(root);
int level = 0;
int lastLevelMember = 0;
while (!q.empty())
{
for (int i = 0; i < count1; i++)
{
int head = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int j = 0; j < supplier[head].list.size(); j++)
{
q.push(supplier[head].list[j]);
count2++;
}
}
level++;
lastLevelMember = count1;
count1 = count2;
count2 = 0;
}
double highestPrice = rootPrice;
for (int i = 0; i < level-1; i++)
{//level会把root也算作1层
highestPrice *= (1 + higherPercent / 100.0);
}
printf("%.2lf %d\n", highestPrice, lastLevelMember);
return 0;
}
[/c]