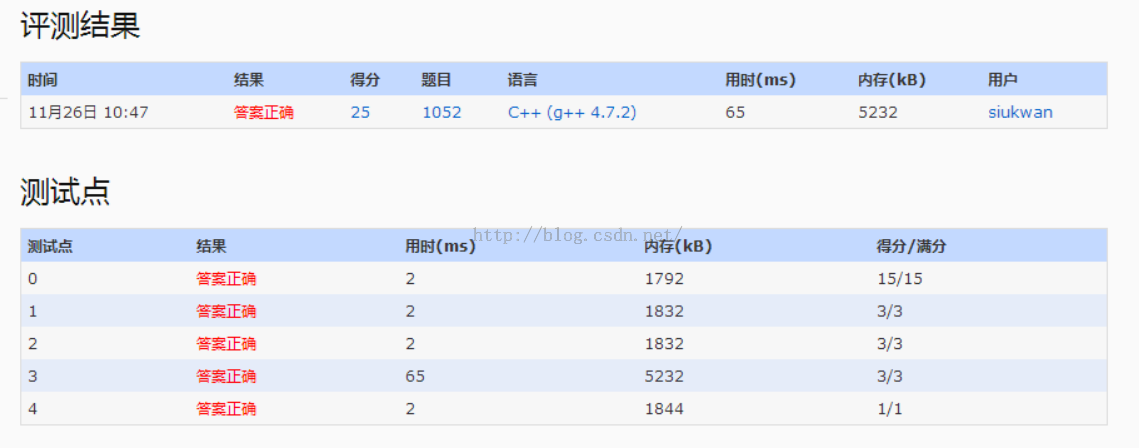
1.题目给出一些节点和其连接的下一个节点地址,求出sort后的链表。
2.这道题目主要有两个难点
1)以head为头部的链表不一样包括全部n个,即输入的数据中存在多个链表,但是我们只需要对以head为头部的链表排序输出即可,这也是为什么结果要求我们输出排序后的链表大小,因为这个大小不一定和n相等;
2)head为-1的情况,卡在这里比较久,需要特殊判断,然后输出0 -1
3.采用建立链表,然后拷贝到vector上进行排序输出。
A linked list consists of a series of structures, which are not necessarily adjacent in memory. We assume that each structure contains an integer key and a Next pointer to the next structure. Now given a linked list, you are supposed to sort the structures according to their key values in increasing order.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive N (< 105) and an address of the head node, where N is the total number of nodes in memory and the address of a node is a 5-digit positive integer. NULL is represented by -1.
Then N lines follow, each describes a node in the format:
Address Key Next
where Address is the address of the node in memory, Key is an integer in [-105, 105], and Next is the address of the next node. It is guaranteed that all the keys are distinct and there is no cycle in the linked list starting from the head node.
Output Specification:
For each test case, the output format is the same as that of the input, where N is the total number of nodes in the list and all the nodes must be sorted order.
Sample Input:
5 00001 11111 100 -1 00001 0 22222 33333 100000 11111 12345 -1 33333 22222 1000 12345
Sample Output:
5 12345 12345 -1 00001 00001 0 11111 11111 100 22222 22222 1000 33333 33333 100000 -1
AC代码:
[c language=”++”]
//#include<string>
//#include<stack>
//#include<unordered_set>
//#include <sstream>
//#include "func.h"
//#include <list>
#include <iomanip>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<set>
#include<queue>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<memory.h>
#include<limits.h>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
struct ListNode{
int val, add;
ListNode*next;
ListNode() :val(0), add(0), next(NULL){};
ListNode(int x) :val(x), add(0), next(NULL){};
};
bool cmp(const ListNode&a, const ListNode&b)
{
return a.val < b.val;
}
int main(void)
{//链表可能断开,需要用头部所在的链表进行排序
int n, head;
cin >> n >> head;
vector<ListNode> list(100001);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{//读取数据
int now, val, next;
scanf("%d %d %d", &now, &val, &next);
list[now].add = now;//保存地址
list[now].val = val;//保存val
if (next != -1)
{//如果next不为-1,则有节点
list[now].next = &list[next];//进行连接
list[next].add = next;//记录next的地址
}
}
vector<ListNode> listOrder(0);//建立一个新的vector
if (head != -1)
{
ListNode* root = &list[head];//记录头部
while (root)//遍历这个链表
{
listOrder.push_back(*root);//压入节点
root = root->next;
}
sort(listOrder.begin(), listOrder.end(), cmp);
printf("%d %05d\n", listOrder.size(), listOrder[0].add);
for (int i = 0; i < listOrder.size(); i++)
{
printf("%05d %d ", listOrder[i].add, listOrder[i].val);
if (i != listOrder.size() – 1)
printf("%05d\n", listOrder[i + 1].add);
else
printf("-1\n");
}
}
else//需要对head==-1进行处理,最后一个测试点考察这个
printf("%d -1\n", listOrder.size());
return 0;
}
[/c]