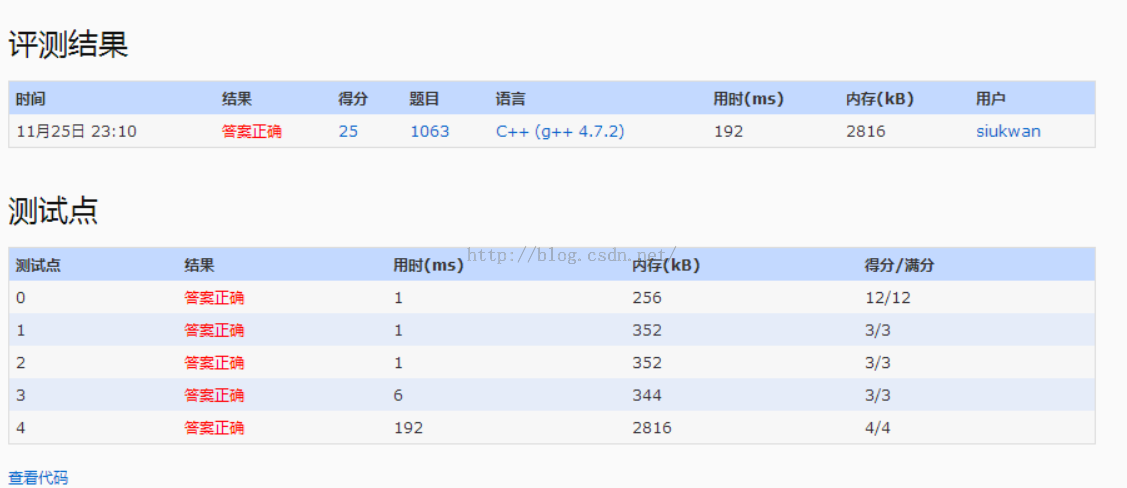
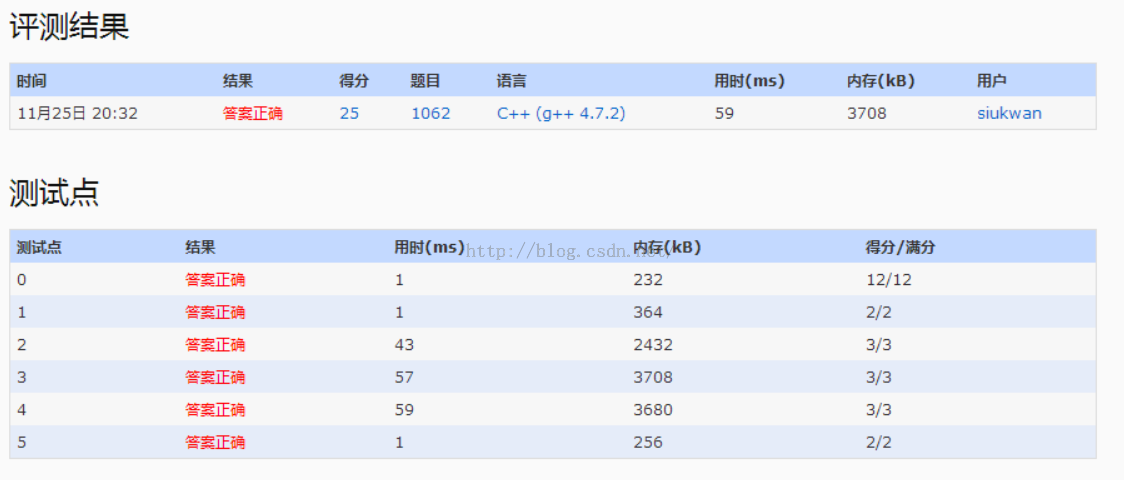
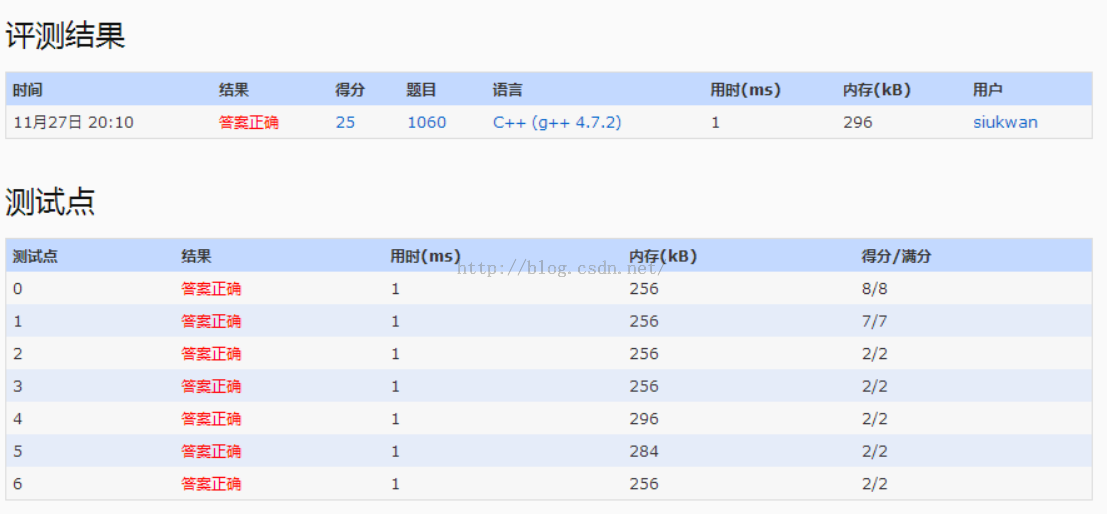
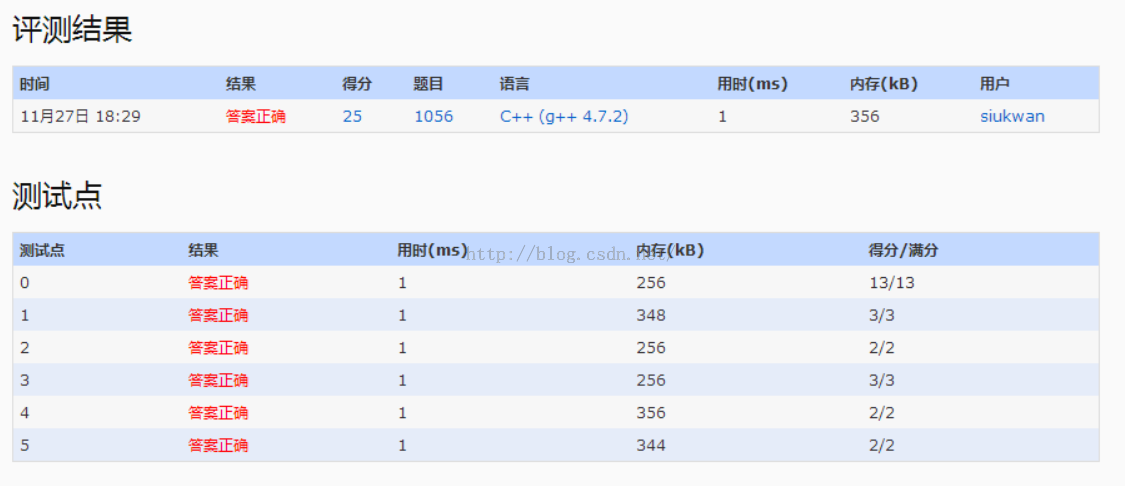
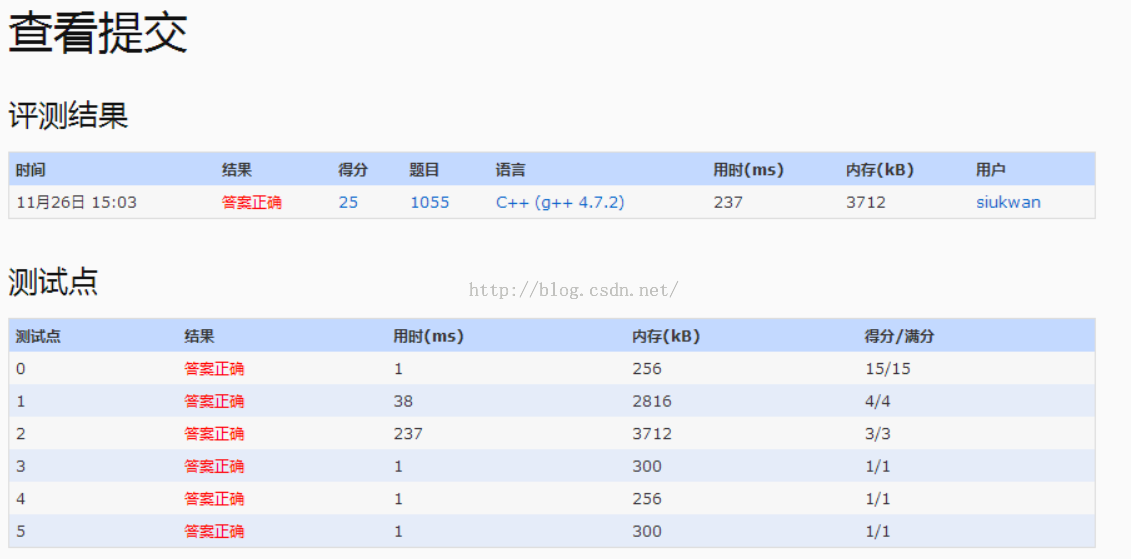
1.该题目主要是先输入一些集合,然后查询某两个集合的交集数量除以并集数量。
2.刚开始使用map去存储每个集合,后面再建立一个新的map合并两个集合的map,从而查找交集数量,结果超时。
3.后面改为利用map作集合的重复判断,在输入集合时,通过map的判断,建立一个每个元素都是唯一的vector。
4.合并时,直接申请两个集合数量总和大小的新vector,把两个集合的vector复制进去,然后进行排序,通过检测元素是否出现两次,来实现检测交集。
5.新vector的size减去交集大小,就是并集。
6.通过这种数据结构和方法,成功AC题目。
Given two sets of integers, the similarity of the sets is defined to be Nc/Nt*100%, where Nc is the number of distinct common numbers shared by the two sets, and Nt is the total number of distinct numbers in the two sets. Your job is to calculate the similarity of any given pair of sets.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. Each case first gives a positive integer N (<=50) which is the total number of sets. Then N lines follow, each gives a set with a positive M (<=104) and followed by M integers in the range [0, 109]. After the input of sets, a positive integer K (<=2000) is given, followed by K lines of queries. Each query gives a pair of set numbers (the sets are numbered from 1 to N). All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each query, print in one line the similarity of the sets, in the percentage form accurate up to 1 decimal place.
Sample Input:
3 3 99 87 101 4 87 101 5 87 7 99 101 18 5 135 18 99 2 1 2 1 3
Sample Output:
50.0% 33.3%
AC代码:
[c language=”++”]
//#include<string>
//#include<stack>
//#include<unordered_set>
//#include <sstream>
//#include "func.h"
//#include <list>
#include <iomanip>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<set>
#include<queue>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<memory.h>
#include<limits.h>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
int main(void)
{
int total;
scanf("%d", &total);
vector<map<int, int>> m(total);
vector<vector<int>> ele(total);
for (int i = 0; i < total; i++)
{
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
int tmp;
scanf("%d", &tmp);
if (m[i][tmp] == 0)
{
m[i][tmp] = 1;
ele[i].push_back(tmp);
}
}
}
int querySum;
scanf("%d", &querySum);
for (int i = 0; i < querySum; i++)
{
int a;
int b;
scanf("%d %d", &a, &b);
a–;
b–;
vector<int> cal(ele[a].size() + ele[b].size());
for (int i = 0; i < ele[a].size(); i++)
{
cal[i] = ele[a][i];
}
for (int i = ele[a].size(); i < ele[a].size() + ele[b].size(); i++)
{
cal[i] = ele[b][i – ele[a].size()];
}
double same = 0;
sort(cal.begin(), cal.end());
for (int i = 0; i < cal.size()-1; i++)
{
if (cal[i] == cal[i + 1])
same++;
}
double ans = same / (cal.size() – same) * 100;
printf("%.1lf%\n", ans);
}
return 0;
}
[/c]